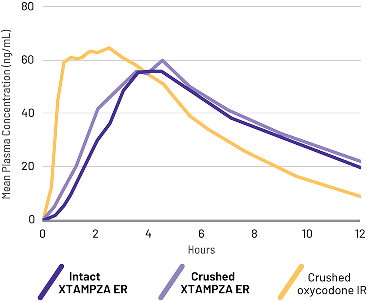
Crushed XTAMPZA ER was bioequivalent to intact XTAMPZA ER
Crushed OxyContin was bioequivalent to crushed IR oxycodone
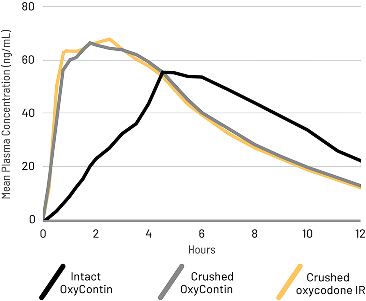
A randomized, open-label, active-controlled, 5-treatment crossover study compared the PK of crushed oxycodone IR to XTAMPZA ER (crushed and intact) and reformulated OxyContin (crushed and intact) taken orally in 42 healthy subjects.2


Appearance of XTAMPZA ER microspheres before and after manipulation with a common household tool. Each microsphere has its own extended-release and manipulation-resistant properties, which are maintained even after crushing.


Appearance of OxyContin tablet before and after manipulation with a common household tool. In a pharmacokinetic study, crushed, reformulated OxyContin dose-dumped, leading to a rapid release of oxycodone.
The oral abuse potential of XTAMPZA ER was evaluated in 2 studies. Below are results from a study with 52 nondependent recreational opioid users who received active and placebo treatment orally. Drug Liking and Take Drug Again were measured on a visual analog scale (VAS).1
Abuse of XTAMPZA ER by injection and by the oral and nasal routes of administration is still possible.
The nasal abuse potential of XTAMPZA ER was evaluated. Below are results from a study with 36 recreational opioid users with a history of intranasal drug abuse who received active and placebo via nasal administration. Drug Liking and Take Drug Again were measured on a VAS.1
Intranasal administration of crushed XTAMPZA ER was associated with statistically lower mean Drug Liking and Take Drug Again scores compared with crushed oxycodone IR1
These findings do not indicate that XTAMPZA ER can entirely prevent abuse via nasal administration. Abuse of XTAMPZA ER by injection and by the oral and nasal routes of administration is still possible.
XTAMPZA® ER (oxycodone) is indicated for the management of severe and persistent pain that requires an opioid analgesic that cannot be adequately treated with alternative options, including immediate-release opioids.
Because the use of XTAMPZA ER exposes patients and other users to the risks of opioid addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death, assess each patient’s risk prior to prescribing and reassess all patients regularly for the development of these behaviors and conditions.
Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression may occur with use of XTAMPZA ER, especially during initiation or following a dosage increase. To reduce the risk of respiratory depression, proper dosing and titration of XTAMPZA ER are essential.
Accidental ingestion of even one dose of XTAMPZA ER, especially by children, can result in a fatal overdose of oxycodone.
Concomitant use of opioids with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Reserve concomitant prescribing of XTAMPZA ER and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
Advise pregnant women using opioids for an extended period of time of the risk of Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated. Ensure that management by neonatology experts will be available at delivery.
Healthcare providers are strongly encouraged to complete a REMS-compliant education program and to counsel patients and caregivers on serious risks, safe use, and the importance of reading the Medication Guide with each prescription.
The concomitant use of XTAMPZA ER with all cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors may result in an increase in oxycodone plasma concentrations, which could increase or prolong adverse drug effects and may cause potentially fatal respiratory depression. In addition, discontinuation of a concomitantly used cytochrome P450 3A4 inducer may result in an increase in oxycodone plasma concentration. Regularly evaluate patients receiving XTAMPZA ER and any CYP3A4 inhibitor or inducer.
To ensure that the benefits of opioid analgesics outweigh the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has required a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) for these products. Under the requirements of the REMS, drug companies with approved opioid analgesic products must make REMS-compliant education programs available to healthcare providers. Healthcare providers are strongly encouraged to do all of the following:
To obtain further information on the REMS and a list of accredited REMS CME/CE, call 1-800-503-0784, or log on to www.opioidanalgesicrems.com. The FDA Blueprint can be found at www.fda.gov/OpioidAnalgesicREM-SBlueprint.
See full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning on Addiction, Abuse and Misuse and other serious risks, accompanying this piece or at XTAMPZAER.com/PI.